Life Insurance Basics

Types of life insurance
To keep things simple there are basically two types of life insurance – permanent and temporary and variations within the two.
In this article we’ll discuss the following concepts:
- Term Insurance
- Permanent Insurance
- Whole Life
- Universal Life
- Indexed Universal Life
- Variable Universal Life
- Underwriting process
- The Cost of Life Insurance
- Simplified and Guaranteed Issue vs. Fully Underwritten
Term Insurance
Term insurance is considered temporary insurance. It lasts only for a term or a specified period of time, usually between 5 and 30 years. At the end of the term your life insurance expires.
During the term you will pay premiums in exchange for insurance that pays an income tax free cash benefit to a beneficiary in the event of your death.
Generally, premiums during a term are level which means they stay the same for the entire term. However, when the term expires so do your benefits. Term policies do not accumulate cash values and are the least expensive type of life insurance you can get.
Term policies are best suited for people who are desiring to cover financial obligations for a loved one in the event of an unexpected death such as a mortgage, student loans, raising children and providing for college expenses for your children. As you get older the need for term insurance diminishes as you pay off those financial obligations.
There are some term insurance policies that provide additional benefits beyond a death benefit. Those policies might have a return of premium benefit and other “living benefits” such as allowing an early withdraw from the face value of the policy prior to a death in the event of a terminal or serious illness.
Some policies might also offer a provision to covert the policy to a permanent policy without undergoing additional underwriting. These are all different options that might increase the cost of the policy, but are worth considering if you need extra protection or desire those benefits.
Permanent Insurance
Permanent life insurance is designed to last throughout one’s life and does not expire. As long as premiums are paid or the policy is paid full the death benefit is guaranteed to be paid to your beneficiary.
One of the benefits of all life insurance is that the face value of the policy is paid out to a beneficiary income tax free. Other than tax free benefits, permanent insurance has some additional benefits that term insurance doesn’t have.
Permanent insurance has a “cash value” component. This allows you to save cash in a policy and grow that cash either through a guaranteed interest rate that the insurer sets, an investment fund or index.
Types of permanent insurance
-
Whole Life Insurance
Premiums are fixed and cash values accumulate with a guaranteed fixed rate within the policy. You may borrow against the policy when your cash values are sufficient for a low interest rate and no qualifying. You may also withdraw cash from the policy, however, if cash values fall to zero and premiums are not paid the policy will expire. Furthermore, if you borrow against the cash value and it is not paid back and you pass away the death benefit is reduced by any outstanding loans. There are different types of whole life products. Whole life policies with mutual companies often offer dividends to an insured which can be paid back to you or paid into the policy to accrue interest. Other policies allow you to pay on the policy for different amounts of time. Such as one time or until a certain age or payments may extend for your whole life. For example, final expense insurance is a specific type of whole life insurance for Seniors that helps pay for funeral or end of life expenses.
Universal Life Insurance
Universal life offers a lot of the same benefits of whole life, but provides more flexibility. You have the opportunity to increase or decrease the premium and death benefit based on your life circumstances. All while the cash value grows tax deferred.
-
Indexed Universal Life Insurance (IUL)
An indexed universal life policy is permanent life insurance that is tied to an index fund (usually the S&P) and accumulates cash value in the policy based on the performance of the fund it’s tied to. The benefits of this type of policy is that it allows you to accumulate cash value within the policy usually at a higher rate than typical whole life policies. The drawback is that the amount of interest you can earn is usually capped, however, if the index drops below zero you do not participate in any loss below zero. For the more risk averse consumer this is big! You participate in market gains but don’t when the market has a down year.
-
Variable Universal Life Insurance (VUL)
A variable universal insurance policy offers more chances at growing the cash value in a policy through different asset allocations within the structure of a policy. This allows part of the cash value to be accumulated in a separate account and be invested in the stock market. These types of policies have the chance of earning more interest on the cash accumulation portion of the policy, but the downside is it is more riskier due to the fact your cash value is subjected to any market losses.
Obtaining Life Insurance
Getting life insurance can be easy if you apply for a simplified or guaranteed issue policy. However, if applying for a policy that offers higher cash accumulation options or higher coverage amounts than the process can be more involved.
Life insurance is a contract between the insurer (life insurance company) and the insured (you or the person who is covered by the policy).
You will need to fill out an application and then go through an underwriting process. That process could be as quick as checking your medical history to something more involved such as getting a medical exam and obtaining an attending physician’s statement.
The level of underwriting requirements are determined by the type of coverage being applied for and company that is issuing the policy.
The Cost of Insurance
Insurance Underwriting - Simplified and guaranteed issue life insurance
In order for insurance company to determine your premiums you will need to obtain a medical exam which could include blood tests, urine or saliva tests. If there are pre-existing health conditions an underwriter might also request records from your physician.
The exact procedures that are necessary to apply for insurance is determined by the insurance company and any tests that are necessary will be explained when you apply. The underwriting process with some companies can take several weeks, if not longer.
Be prepared when applying for coverage that there could be a wait time before you are insured.
When an insurance company orders a physical and medical tests to determine how much coverage and premiums you will pay this is considered to be a “fully underwritten” policy. Many insurance plans fall under this category.
However, a lot more insurance companies these days are offering policies that do not require full medical exams.
Life insurance policies that can be issued without medical examinations are considered “simplified issue” because of the less restrictive and time consuming underwriting process.
Obtaining a policy is considerably more “simple” since all that is required is answering some health questions and running a quick background and prescription check. You can be approved for a policy in minutes versus weeks.
These policies are great for older individuals, those with some health issues and anyone who doesn’t want to undergo a medical examination. The trade off is the rates are slightly higher and the amount of coverage you can obtain is limited.
However, in some cases the rates can be just as competitive as fully underwritten plans. It just depends on the company, your health and amount of coverage being requested.
For example, if you’re looking for a 200k term policy then it’s possible to qualify for a simplified issue policy. However, if you are looking for a 1 million dollar insurance policy then most insurance companies will want you to undergo additional underwriting such as an exam in addition to your application to properly assess your premium rating.
A guaranteed issue insurance policy is the most lenient type of policy. However, there are coverage restrictions and usually a waiting period on how long you must have the policy in force before the benefits are available. The rates are also the highest.
These types of policies should only be used when an individual can not qualify for any other types of insurance.
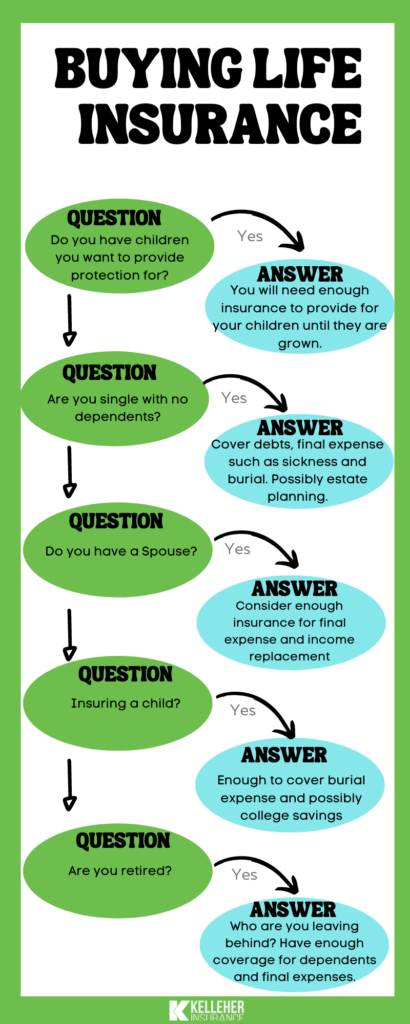
Which insurance plan is right for you?
Which type of life insurance and how much should you consider?
Your specific life circumstance, financial and retirement goals will determine which type of life insurance policy is best for you.
Therefore, the best way to make sure you’re getting the right type of coverage for yourself and your family is to make an appointment today to discuss what your options are and what makes more sense based on your individual needs, risk tolerance and retirement goals.
Life insurance rates are determined by many factors. In order to get the best rates a policy needs to go through more strict underwriting standards.
This means answering questions about your health, lifestyle and occupation. It also means you will undergo a medical exam to determine your current health status and risk factors for rating your policy.
Your age, gender and hobbies can also contribute to whether an insurance company might deem you more of a risk or not. Generally speaking, the younger and healthier you are the better your rate will be.
Also, if you have any type of severe health condition, terminal illness, risky job or hobby, you might not qualify at all for life insurance.
The cost and whether you qualify is up to an insurer (insurance carrier). This will vary between different companies, types of plans and coverages offered.